Security Scanning
Overview
Docker Registry UI includes built-in vulnerability scanning powered by Trivy, providing comprehensive security analysis of your container images.
Quick Start with Trivy
Trivy is built into the Docker Registry UI container. No additional setup required!
Scanning Images
- Navigate to the repository
- Find the tag you want to scan
- Click the "Scan" button (shield icon 🛡️) next to the tag
- Wait for the scan to complete (usually 10-30 seconds)
- View vulnerability badges showing counts by severity
What Trivy Detects
- OS Packages: Alpine, RHEL, CentOS, Ubuntu, Debian, Amazon Linux, etc.
- Application Dependencies: npm, pip, gem, composer, maven, etc.
- Known CVEs: From National Vulnerability Database and other sources
- Severity Levels: Critical, High, Medium, Low, Unknown
Vulnerability Display
Scan results are displayed as color-coded badges:
- Critical: Red badge - Immediate action required
- High: Orange badge - High priority fixes
- Medium: Yellow badge - Medium priority
- Low: Blue badge - Low priority
- Unknown: Gray badge - Severity not determined
CVE Details
Click on any vulnerability badge to view detailed information:
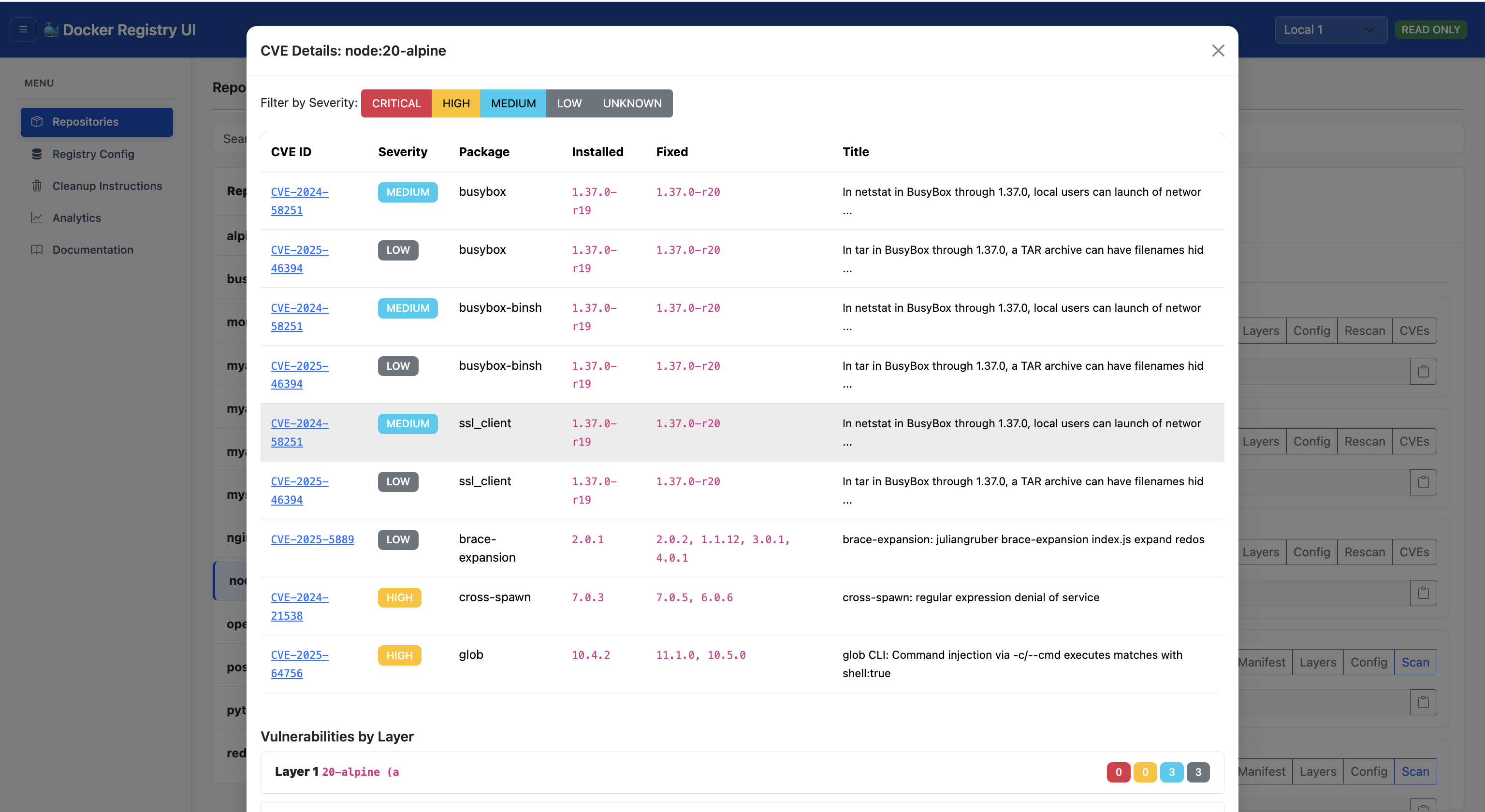
- CVE ID: Clickable link to National Vulnerability Database
- Package: Affected package name and version
- Severity: Vulnerability severity level
- Fixed Version: Version that fixes the vulnerability
- Description: Detailed vulnerability description
- Layer: Which image layer introduced the vulnerability
Layer-by-Layer Analysis
View which layer introduced each vulnerability:
- Click "View Layers" for any tag
- See vulnerability counts per layer
- Identify which Dockerfile commands introduced vulnerabilities
- Optimize your Dockerfile to reduce vulnerabilities
Scan Results Storage
Scan results are persisted to disk:
- Stored in the same directory that contains the configured
CONFIG_FILE(for example, ifCONFIG_FILE=/app/data/registries.config.jsonthen results are written under/app/data). - One JSON file per image tag. Filenames use the pattern
<repo_with_slashes_replaced_by_underscores>_<tag>.json(e.g.myrepo_subrepo_latest.json). - Results remain available after UI restart
- Re-scanning overwrites previous results
Troubleshooting
Scanner Not Responding
- Verify Trivy is installed in container
- Check network connectivity to registry
- Verify image exists and is accessible
- Check container logs for errors
Scan Takes Too Long
- First scan downloads vulnerability database (slower)
- Subsequent scans use cached database (faster)
- Large images take longer to scan
- Network speed affects download time
Best Practices
- Scan Regularly: New vulnerabilities are discovered daily
- Fix Critical First: Prioritize critical and high severity issues
- Update Base Images: Use latest stable base images
- Minimize Layers: Fewer layers = smaller attack surface
- Remove Unnecessary Packages: Only install what you need
- Use Specific Versions: Avoid
latesttags in production